Our bodies are amazing machines, but like any machine, they can wear down or get injured. Orthopedic injuries affect the musculoskeletal system’s bones, muscles, ligaments, tendons, joints, and nerves. Today, we’ll delve into three frequent orthopedic injuries: ACL tears, rotator cuff injuries, and arthritis.
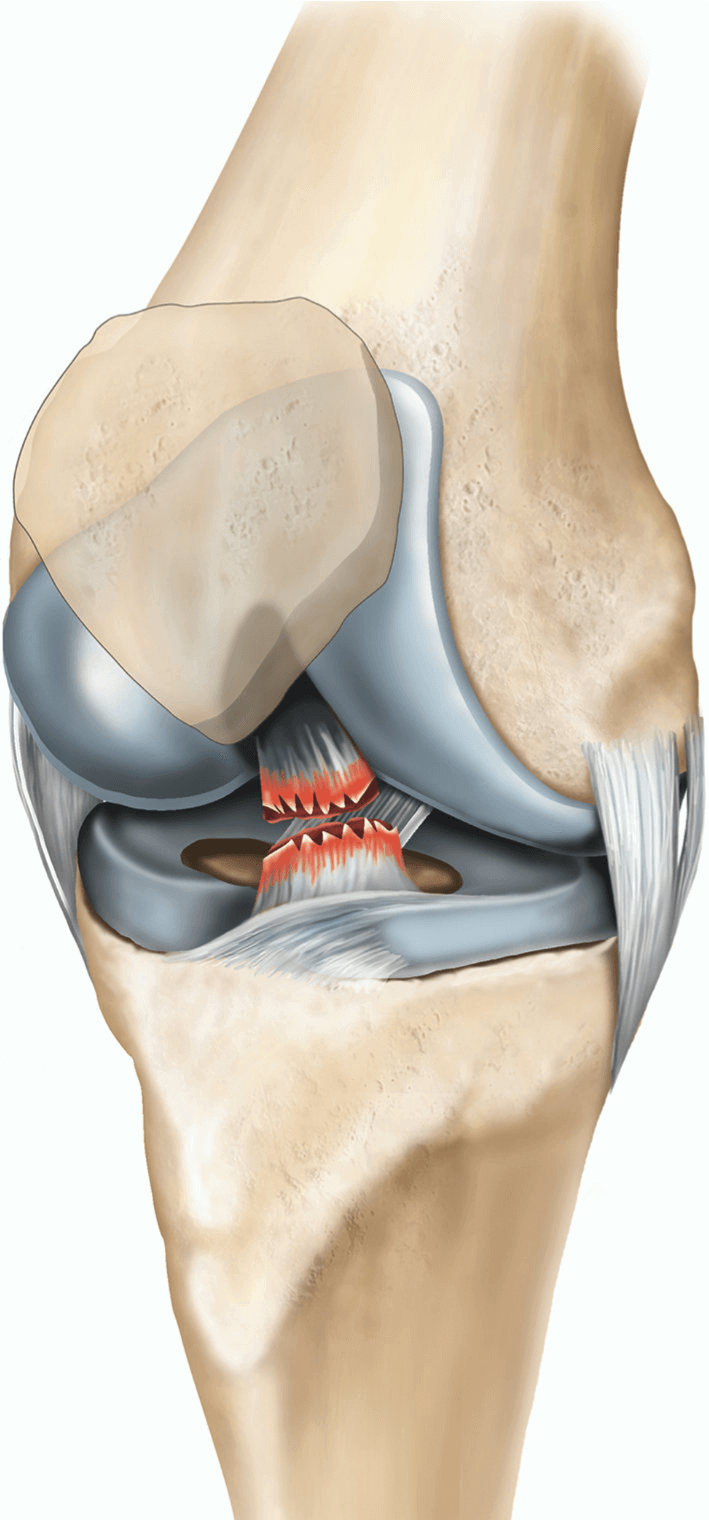
- ACL Tears: The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is a crucial knee stabilizer. A tear can occur during sudden stops, pivoting, or landing wrong.
- Causes: Sports injuries, especially in sports with quick changes in direction (basketball, soccer).
- Symptoms: Popping sound at injury, severe knee pain, swelling, instability, difficulty bearing weight.
- Treatment Options: RICE (rest, ice, compression, elevation) for initial inflammation. Physical therapy is often the first line of treatment to strengthen surrounding muscles and improve stability. In some cases, surgery is needed to reconstruct the ACL.
- Rotator Cuff Injuries: The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that allow shoulder movement. Repetitive overhead motions can damage this delicate area.
- Causes: Overuse in athletes (baseball pitchers, tennis players) or people with physically demanding jobs. Age-related wear and tear is also a factor.
- Symptoms: Pain when lifting the arm overhead, weakness, crackling sensation, difficulty sleeping on the affected side.
- Treatment Options: Rest, pain medication, and physical therapy to strengthen the rotator cuff muscles. In severe cases, surgery may be needed to repair a torn tendon.

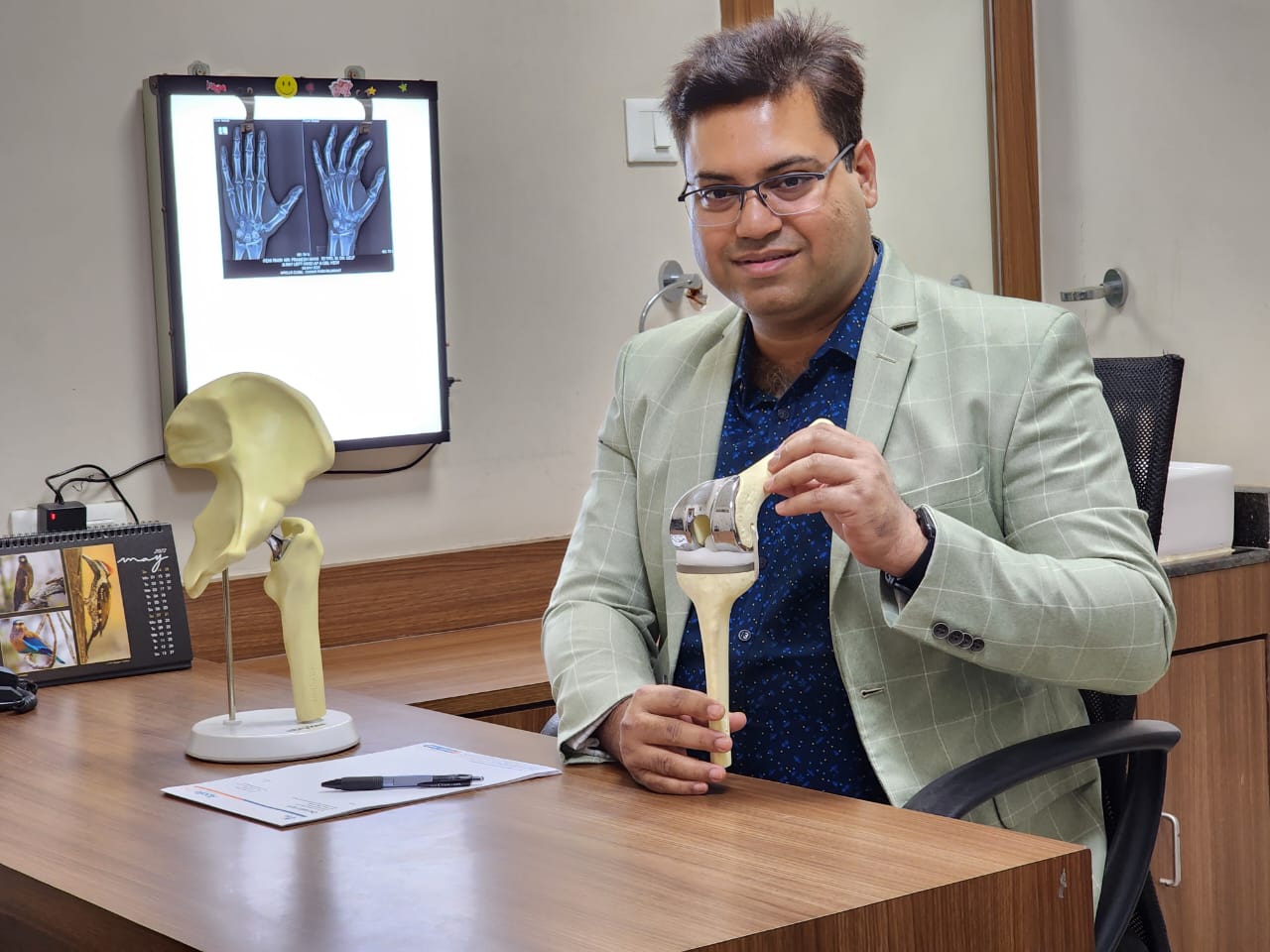
- Arthritis: Arthritis, a thief of mobility, is a widespread condition marked by inflamed joints. It relentlessly brings pain, stiffness, and a restricted range of motion. There are several types of arthritis, the most common being osteoarthritis (wear-and-tear) and rheumatoid arthritis (an autoimmune disease).
- Causes: Age, previous joint injury, obesity, genetics. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease where the body’s defense system mistakenly targets the joint lining, leading to inflammation and damage.
- Symptoms: Pain, stiffness, swelling, decreased range of motion, crackling sounds in the joint.
- Treatment Options: There’s no cure for arthritis, but treatments can manage symptoms. These include pain medication, physical therapy, injections, weight management, and joint replacement surgery in severe cases.
Conclusion:
This blog provides general information. If you suspect an orthopedic injury, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention can often lead to a faster and more complete recovery.